Hydroelectric Power: Pros and Cons
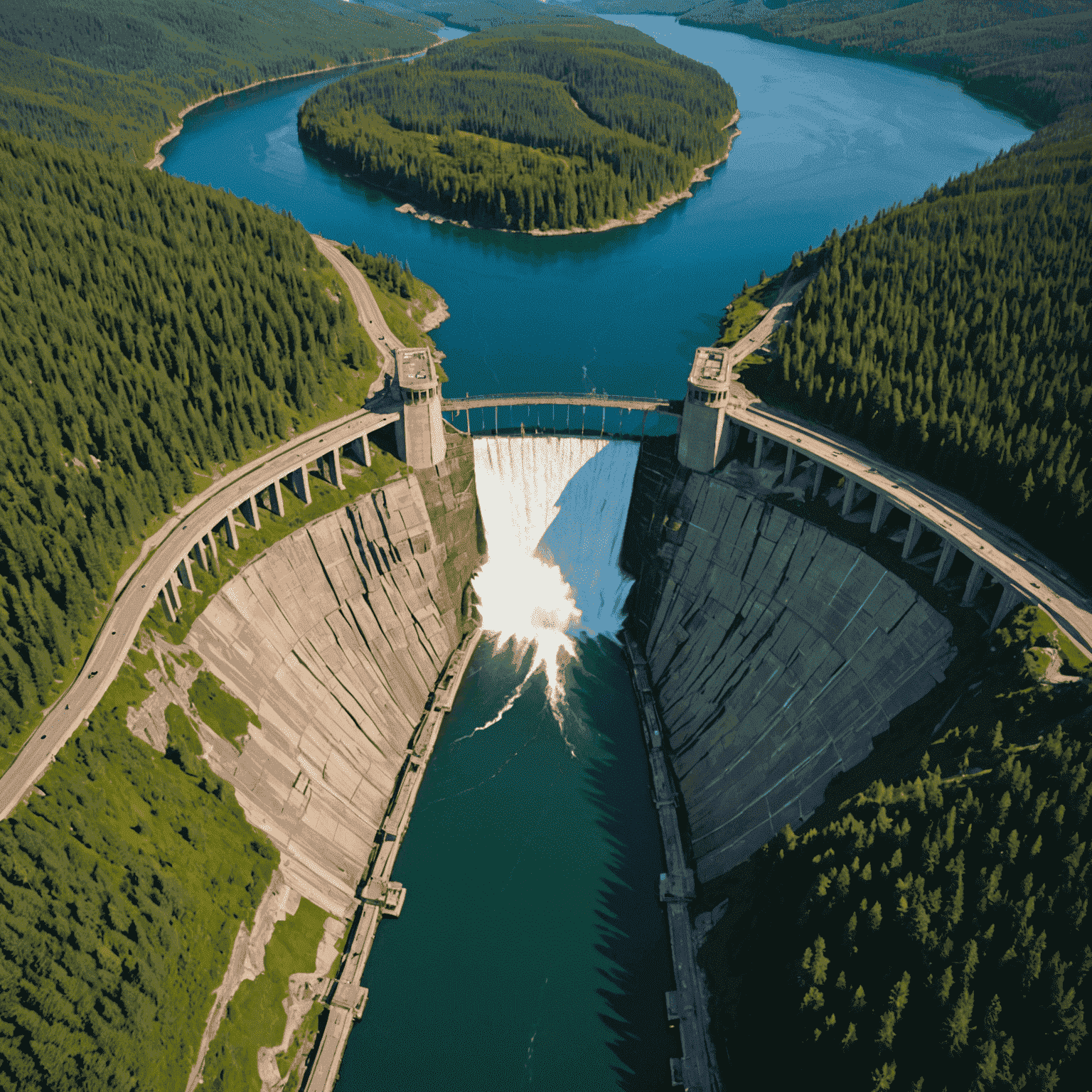

Investing in hydroelectric power projects, particularly in Canada, offers a unique set of advantages and challenges. As we delve into this green energy investment opportunity, it's crucial to understand both sides of the coin.
Advantages of Hydroelectric Power
- Clean and Renewable: Hydroelectric power is a clean energy source that doesn't produce greenhouse gases during operation.
- Long-lasting Infrastructure: Dams and hydroelectric facilities can last for decades, providing a long-term return on investment.
- Energy Storage Capability: Reservoirs act as a form of energy storage, allowing for power generation when needed most.
- Low Operating Costs: Once built, hydroelectric plants have relatively low operating and maintenance costs.
- Canadian Expertise: Canada has extensive experience in hydroelectric projects, making it a leader in this green energy sector.
Challenges and Considerations
- High Initial Costs: Building dams and hydroelectric facilities requires significant upfront investment.
- Environmental Impact: Large-scale projects can affect local ecosystems and wildlife habitats.
- Dependence on Water Levels: Power generation can be affected by droughts or changes in precipitation patterns.
- Social Considerations: Some projects may require the relocation of communities or impact indigenous lands.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex environmental regulations and obtaining necessary permits can be time-consuming.
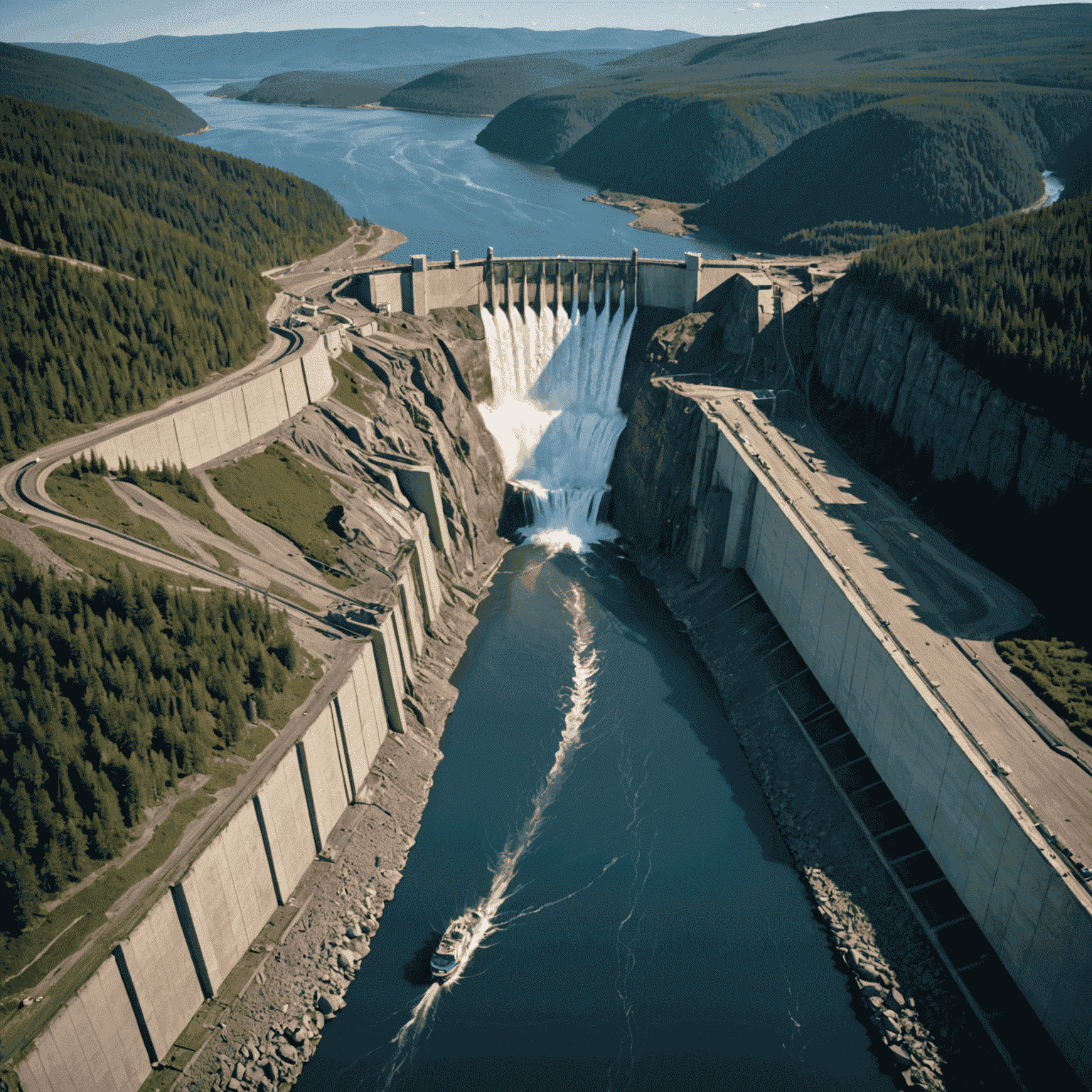
Canadian Initiatives in Hydroelectric Power
Canada has been at the forefront of hydroelectric power development, with several notable projects:
- Site C Clean Energy Project (British Columbia): A large-scale dam and hydroelectric generating station on the Peace River.
- Muskrat Falls Project (Newfoundland and Labrador): A significant hydroelectric facility on the Lower Churchill River.
- La Romaine Complex (Quebec): A series of four hydroelectric powerhouses on the Romaine River.
Investment Considerations
When considering investments in hydroelectric power projects, especially in Canada, keep these factors in mind:
- Long-term Vision: Hydroelectric investments typically require a long-term perspective due to the extended construction and operational phases.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate environmental, social, and regulatory risks associated with specific projects.
- Technological Advancements: Consider investments in projects that incorporate modern technologies for improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
- Diversification: Balance hydroelectric investments with other green energy options to mitigate risks.
- Government Support: Research available incentives and support for renewable energy projects in different Canadian provinces.
Conclusion
Investing in hydroelectric power projects in Canada offers a compelling opportunity to participate in the green energy revolution. While challenges exist, the long-term benefits and Canada's expertise in this sector make it an attractive option for those looking to diversify their energy investments. As with any investment, thorough research and careful consideration of all factors are essential for making informed decisions in this dynamic and crucial field of renewable energy.